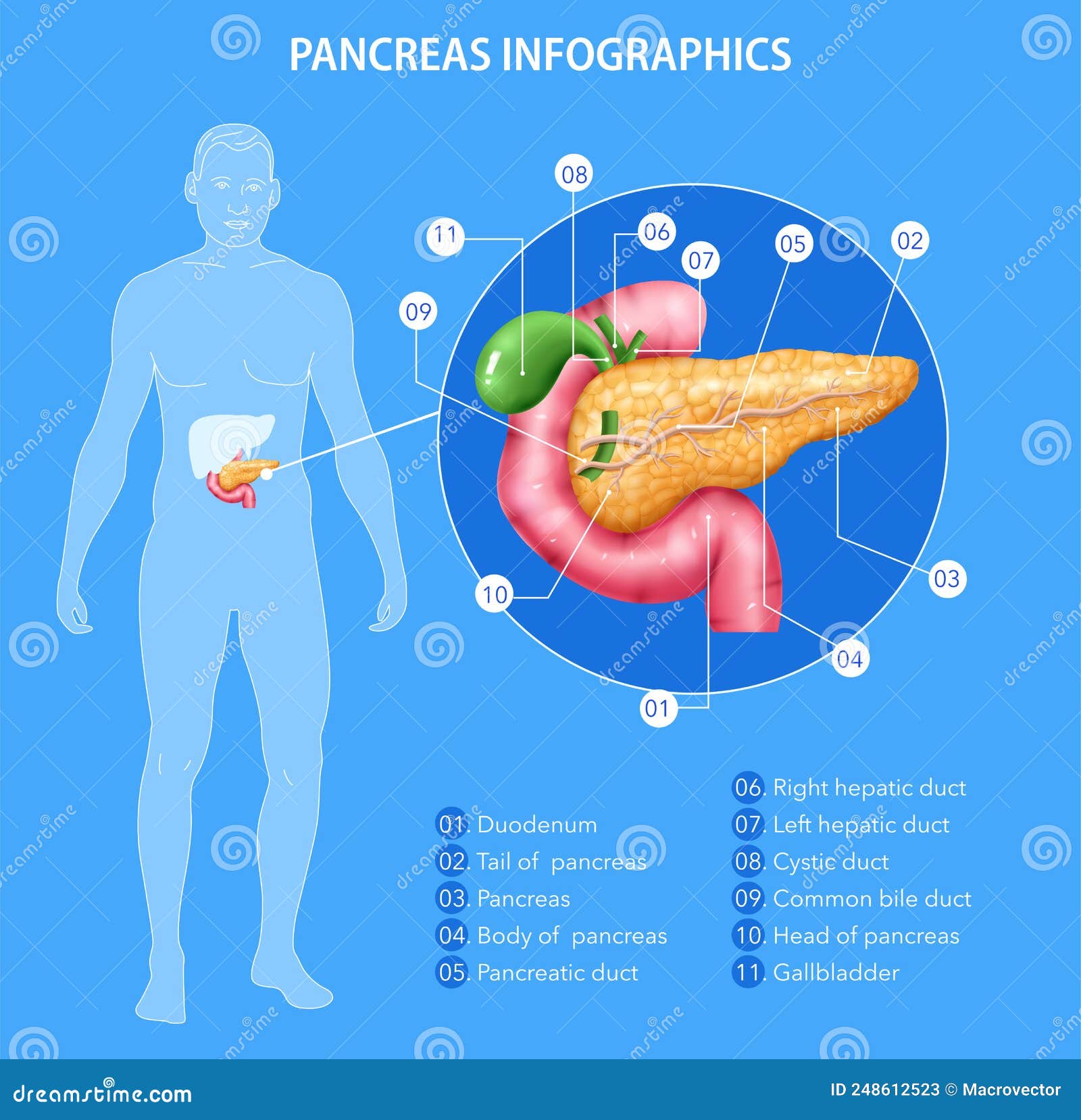
Pancreas Anatomy In Complex With Intestine And Bile Duct Human Healthy Biology Diagrams Detailed anatomical description of human pancreas, including simple definitions and labeled, full-color illustrations. Measles Cases on the Rise Anatomy of the pancreas. The pancreas is an elongated, tapered organ located across the back of the belly, behind the stomach. The right side of the organ—called the head—is the widest part of
The pancreas is an accessory organ and exocrine gland of the digestive system, as well as a hormone producing endocrine gland.It is a retroperitoneal organ consisting of five parts and an internal system of ducts. The pancreas is supplied by pancreatic arteries stemming from surrounding vessels and is innervated by the vagus nerve (CN X), celiac plexus, and superior mesenteric plexus. Pancreas anatomy. Parts of the pancreas include the: Head: The wider part of your pancreas that sits in the curve of your duodenum. On average, a healthy human pancreas weighs around 91.8 grams (0.20 pounds). That's about the same as a deck of playing cards. Conditions and Disorders. The Stomach, Gallbladder, and Pancreas Explore the anatomy and roles of the stomach, gallbladder, and pancreas with Innerbody's interactive 3D model. by Tim Taylor Last The stomach, gallbladder, and pancreas are three of the most important digestive organs in the human body. These organs work together to produce and store secretions that

The Pancreas: Anatomy and 3D Illustrations Biology Diagrams
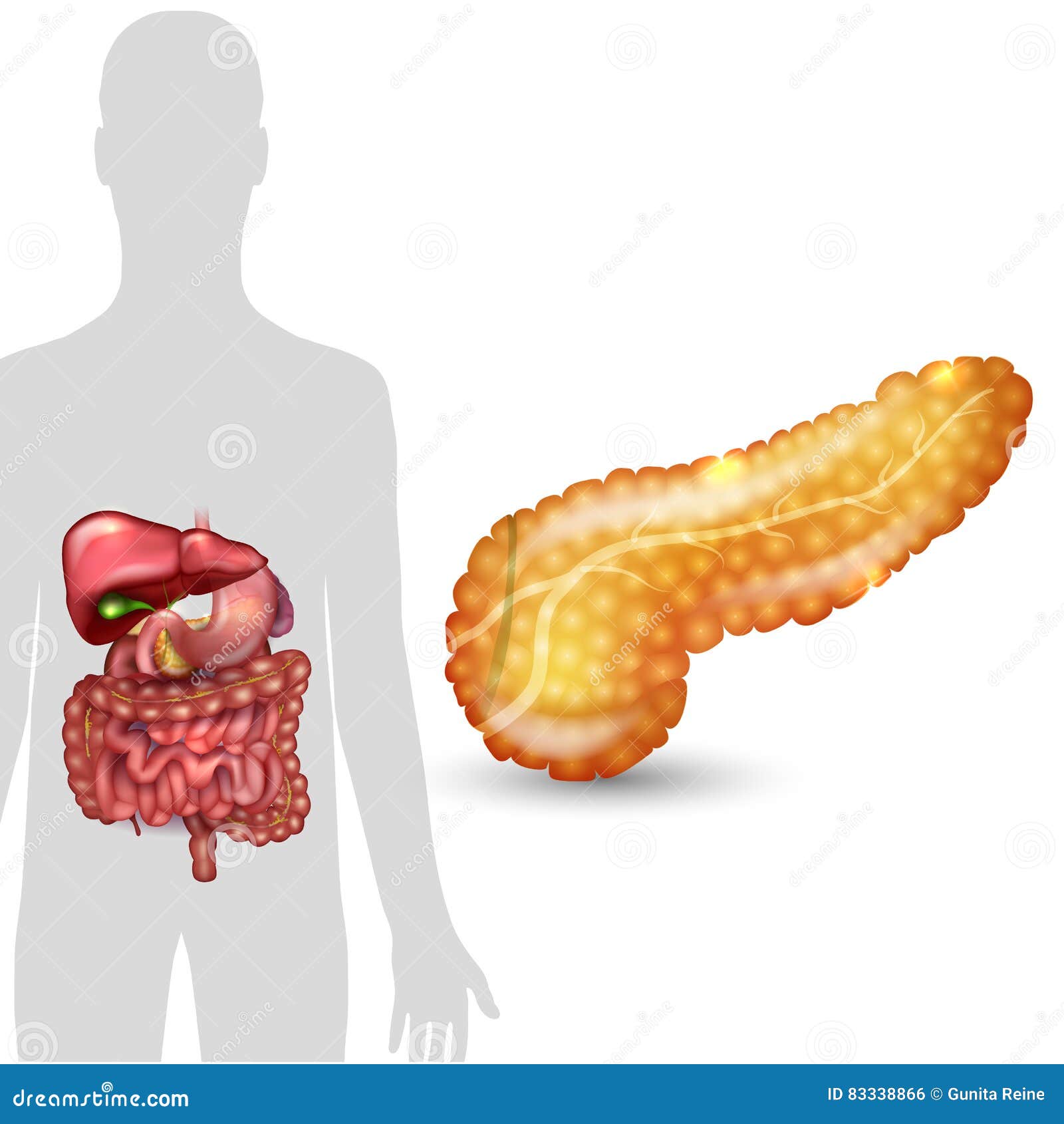
Pancreas Anatomy. The pancreas measures about 20 centimeters in length (about 8 inches) and weighs between 75 to 90 grams (heavier in men). The bulk of the pancreatic tissue is dedicated to its exocrine function, while only 1% to 2% of the pancreas is responsible for the endocrine component. Human Intestinal Parasites - Causes, Symptoms

The pancreas (plural pancreata) is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e., it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. [2] 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1%

Pancreas: Function, Location, Anatomy & Living Without One Biology Diagrams
Gross Anatomy. The pancreas is a narrow, 6-inch long gland that lies posterior and inferior to the stomach on the left side of the abdominal cavity. The pancreas extends laterally and superiorly across the abdomen from the curve of the duodenum to the spleen. The head of the pancreas, which connects to the duodenum, is the widest and most The pancreas is a vital glandular organ in the human body that serves both endocrine and exocrine functions. It plays a critical role in digestion and metabolism. [2] Structurally, it is soft, elongated, and tapered, with a lobular appearance due to its glandular tissue.The pancreas is composed of acinar cells, which produce digestive enzymes, and pancreatic islets, which regulate hormone