Do You Know Why Your CNC Spindles Fail Ask the Experts Biology Diagrams What happens if spindle fibers malfunction during mitosis? If spindle fibers malfunction, it can lead to improper chromosome distribution, resulting in aneuploidy. This condition can cause serious consequences, including genetic disorders and cancer. Cells may also experience cell cycle arrest, halting division until the issue is resolved.

The spindle fibers play a crucial role in ensuring that each chromosome is correctly positioned and separated during cell division. When faulty spindle fibers fail to properly align the chromosomes, errors such as unequal distribution of genetic material or incomplete separation can occur. These errors can lead to aneuploidy and chromosomal

What Is The Function Of Spindle Fibers During Mitosis? Biology Diagrams
Spindle fibers pull the chromosomes toward the equator. This creates tension and aligns them in a straight line. This precise alignment ensures each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes. Any malfunction can lead to genetic disorders. By learning about it, we appreciate the complexity of life. Knowledge of spindle apparatus
Spindle orientation is regulated by a conserved set of molecules in metazoans. (A) The C. elegans one-cell embryo is polarized along the anterior-posterior axis and divides asymmetrically in a somatic anterior cell (AB) and a posterior germline precursor cell (P1). The conserved PAR (partitioning defective) proteins are localized asymmetrically at the cortex: PAR-3, PAR-6, and PKC-3 at the

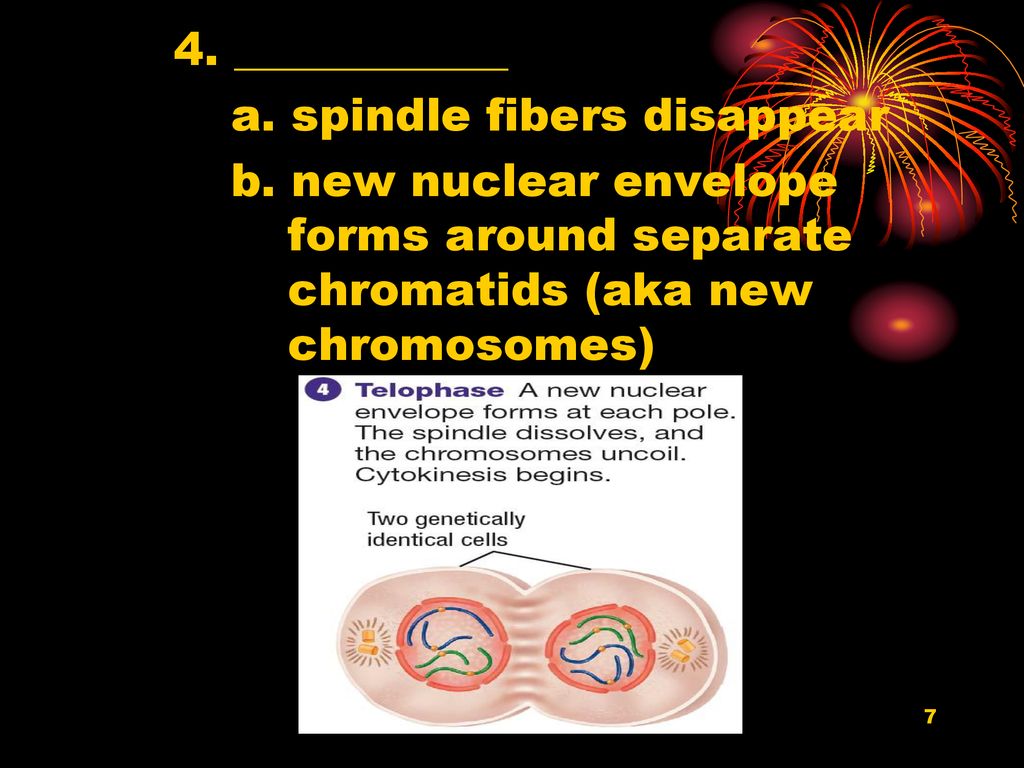
Prophase 2: Key Chromosome Behaviors and Spindle Realignments Biology Diagrams
Spindle fiber is a network of filaments that are formed during the cell division process. They help in the movement of chromosomes during both mitosis and meiosis. Q2 . What are spindle fibers made of? Spindle fiber is most abundantly composed of the microtubule, which is a polymer of 𝜶 and 𝞫-tubulin dimer. Also, the spindle fiber is made The spindle is formed during prophase of mitosis and meiosis, and its role is crucial for the correct separation of chromosomes. Components of the Spindle. The spindle is composed of three main components: Microtubules: These are the primary building blocks of the spindle, forming a network of fibers that connect the centromeres of the chromosomes. In prophase 1, spindle fibers attach to homologous chromosomes, while in prophase 2, they reorient to attach to sister chromatids. This reorientation is crucial for the segregation of chromatids during anaphase 2. Research highlights the importance of these proteins, illustrating how their malfunction can lead to aneuploidy, which affects
